

In the table below, we take a look at how the average price of grid-tied solar panels varies by system size. However, solar system costs can vary a lot based on many factors, such as system size, the state you live in, the brand of solar panels you choose, and even the pitch of your roof. Most systems cost between $2.75 and $3.35, with a national average price of around $3.00 per watt as of 2023. The average cost of a typical grid-tied solar system is between $12,600 and $14,000 net of the federal solar tax credit.

How much does a grid-tied solar system cost? This makes grid-tied solar systems both cheaper and simpler to install.
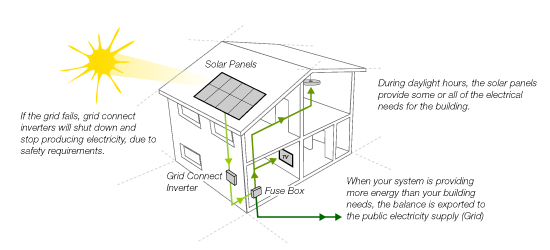
Complex modern grids with a mix of traditional generation and DER can make responding to abnormal situations like storms or blackouts more difficult. Increasing amounts of solar and DER on the grid lead to both opportunities and challenges for grid reliability. The electrical grid must be able to reliably provide power, so it’s important for utilities and other power system operators to have real-time information about how much electricity solar systems are producing. This means that developing batteries or thermal storage is key to adding more solar. Since solar energy can only be generated when the sun is shining, the ability to store solar energy for later use is important: It helps to keep the balance between electricity generation and demand. Inverters convert DC electricity, which is what a solar panel generates, to AC electricity, which the electrical grid uses. One type of power electronic device that is particularly important for solar energy integration is the inverter. By 2030, as much as 80% of electricity could flow through power electronic devices. This could include converting between high and low voltage, regulating the amount of power flow, or converting between direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC) electricity, depending on where the electricity is going and how it will be used. Increased solar and DER on the electrical grid means integrating more power electronic devices, which convert energy from one form to another. However, systems like rooftop solar now require the grid to handle two-way electricity flow, as these systems can inject the excess power that they generate back into the grid. Traditionally, electricity only needed to flow one way through these systems: from the central generation source to the consumer. Substations and transformers convert power between high and low voltage. The distribution grid refers to low-voltage lines that eventually reach homes and businesses. These high voltages allow power to be transported long distances without excessive loss. The transmission grid is the network of high-voltage power lines that carry electricity from centralized generation sources like large power plants. The electrical grid is separated into transmission and distribution systems. These smaller-scale and dispersed energy sources are generally known as distributed energy resources (DER). In addition to large utility-scale plants, modern grids also involve variable energy sources like solar and wind, energy storage systems, power electronic devices like inverters, and small-scale energy generation systems like rooftop installations and microgrids. Modern electrical grids are much more complex. The Electrical Gridįor most of the past 100 years, electrical grids involved large-scale, centralized energy generation located far from consumers. What is solar systems integration and how does it work? Solar systems integration involves developing technologies and tools that allow solar energy onto the electricity grid, while maintaining grid reliability, security, and efficiency.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
